
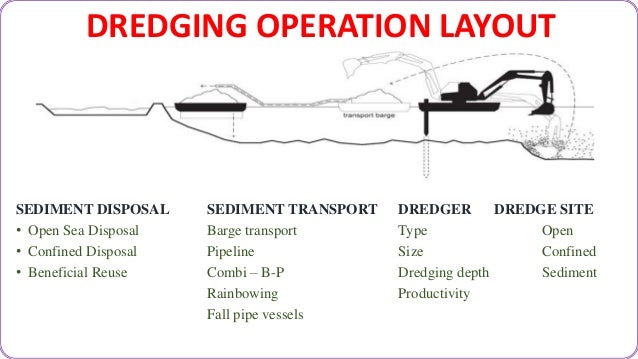
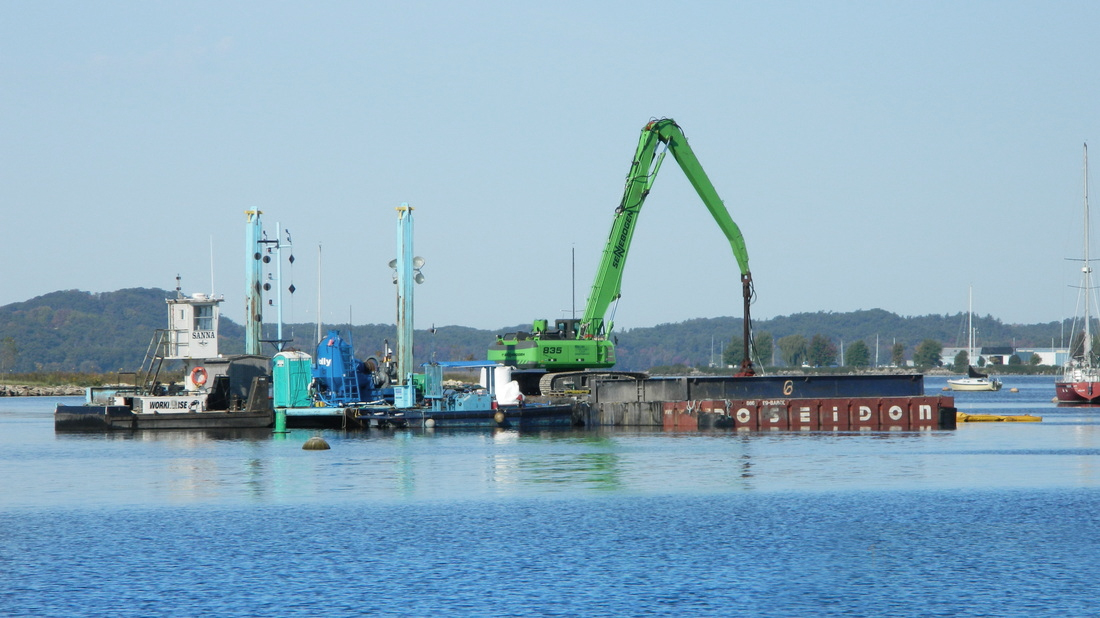
Continually increasing vessel size and draft has created a need to deepen navigation channels and berths in ports. Removal of sediment for new construction activities or deepening of navigation channels is referred to as capital dredging. Ports have a legal obligation to maintain navigation channels and berths at advertised depth, thus removal of sediment settled in navigation channels and berths falls to port authorities and marina owners in what is referred to as maintenance or navigation dredging.

Sediment accumulated from riverine deposition, as well as sediment moved by coastal dynamics can cause shallowing of navigation channels and berths. Sediment is also transported locally within the marine environment.

Deposition in lower energy areas can cause build-up of sediment in estuaries and harbours. The elements of the natural sediment movement processes most relevant to the marine environment are erosion, transportation and deposition (riverine, estuary and coastal). Sediment is an essential, integral and dynamic part of the ecosystem. Since 1986, the OSPAR Convention has encouraged Contracting Parties to minimise adverse impacts on the marine environment through its guidelines for management of dredged material and through actions addressing substances found in dredged material at source. There is also potential for contaminants to be transferred and redistributed by re-suspension and uptake by biota. Adverse impacts from the dumping or placement of the dredged material can be physical (through smothering of habitats and organisms), chemical (through toxicity) and / or biological (though increased turbidity, and from bioaccumulation and biomagnification of contaminants through the food web).ĭumping or placement of sediments on the seabed will bury benthos and can lead to damage to habitats and biological communities, especially at newly designated sites. Most dredging activities result in the material being dumped or placed at designated sites within the marine environment. This results in the need to dredge referred to as maintenance or navigation dredging. Ports and waterway authorities have a legal obligation to maintain navigation channels. Sediments, although not in themselves polluting materials, are sinks for some contaminants bound to the sediment particles that end up in waterways, harbours, ports and seas mainly from anthropogenic sources such as sewage discharges, storm-water overflows, marine traffic, agricultural run-off, industrial wastewater and historically poor environmental management. Sediment is an integral and dynamic part of the ecosystem, and through various natural processes can build-up in estuaries and harbours.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
